References
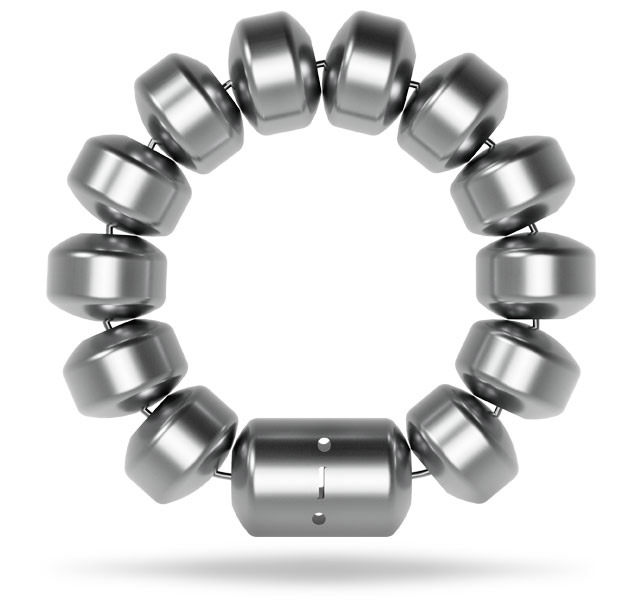
1. No device erosions, migrations, or malfunctions occurred in this study. Device removal occurred in 7 patients. Bothersome heartburn decreased to 11.9% at 5 years from 89% (p<0.001 and bothersome regurgitation decreased to 1.2% at 5 years from 57% (p<0.001). (n=100)
2. Ganz R. Edmundowicz S, Taiganides P, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Patients Receiving a Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation Device for Gastroesophageal Reflux. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. 14(5):671-7. Based on a study observing 100 patients who were implanted with LINX, daily use of PPIs decreased to 15.3% at 5 years. (p<0.001)
3. Ganz R. Edmundowicz S, Taiganides P, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Patients Receiving a Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation Device for Gastroesophageal Reflux. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. 14(5):671-7. Based on a 5 year prospective, multi-center, single-arm study observing 100 patients who were implanted with LINX, regurgitation was 57% at baseline and decreased to 1.2% at 5 years. (p<0.001)
4. Ganz R. Edmundowicz S, Taiganides P, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Patients Receiving a Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation Device for Gastroesophageal Reflux. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. 14(5):671-7. Based on a 5 year prospective, multi-center, single-arm study observing 100 patients who were implanted with LINX, there was a significant improvement in the median GERD-HRQL score at 5 years, as compared with baseline, both with and without PPI use, 4 vs 11 and 27 respectively (p<0.001).